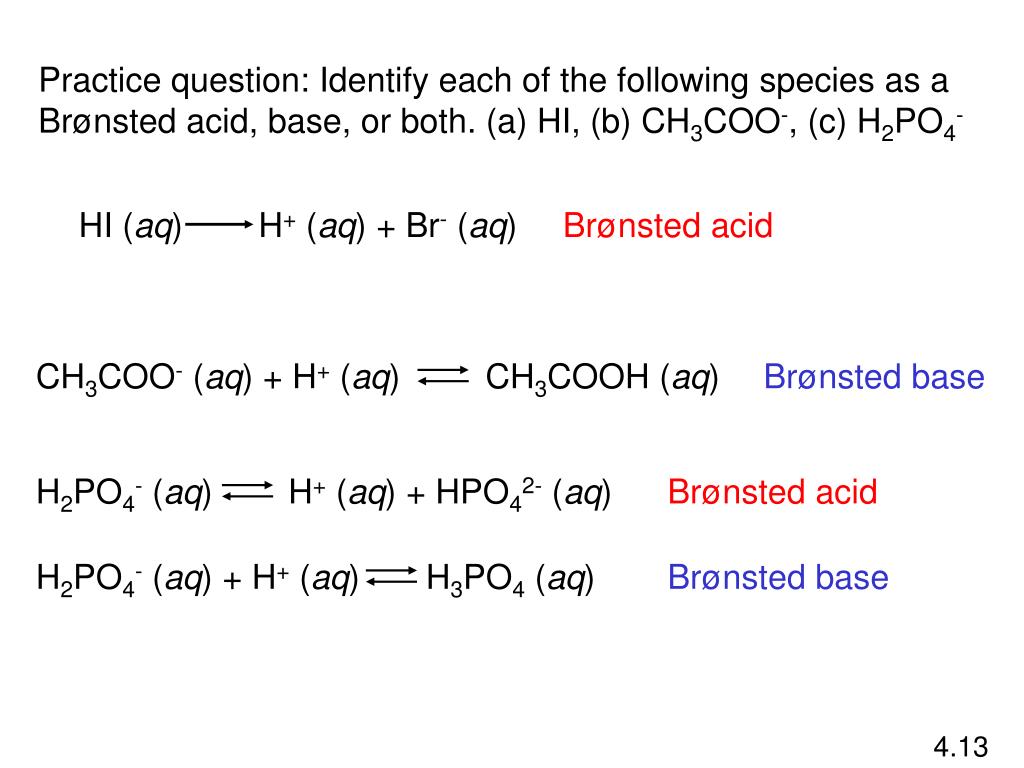
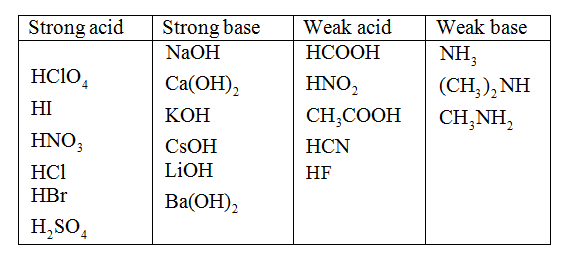
HI (aq) Phosphorous acid H 3 PO 3 Carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 Sulfuric acid H 2 SO 4 Formic acid HCOOH Name each of the following acids HClO 4 perchloric acid HCOOH formic acid H 3 PO 4 phosphoric acid HCl (aq) hydrochloric acid H 3 BO 3 boric acid H 2 SO 4 sulfuric acid HNO 2 nitrous acid HI (aq) hydroiodic acid CH 3 COOH acetic acidSo, Is NH 4 an acid or base?Classify each substance as a strong acid, strong base, weak acid,or weak baseStrong Acid Question Classify each substance as a strong acid, strong base, HI HCl H 2 SO 4 Weak Acid HClO 4 HCOOH HF HCN HNO 2 CH 3 COOH Strong Base Ca(OH) 2 LiOH NaOH KOH CsOH (CH 3) 2 NH Ba(OH) 2 Weak Bases NH 3 CH 3 NH 2 Please, let me

Is Hi Hydroiodic Acid A Strong Or Weak Acid Youtube
Is hi(aq) an acid or base
Is hi(aq) an acid or base-Acids are defined as compounds that donate a hydrogen ion (H ) to another compound (called a base ) Traditionally, an acid (from the Latin acidus or acere meaning sour) was any chemical compound that, when dissolved in water, gives a solution with a hydrogen ion activity greater than in pure water, ie a pH less than 70Water can act like an acid when it donates Hor as a base when it receives H Substances that can act as both acids and bases are amphoteric Water is the most common amphoteric substance and its behavior depends on the other reactant Water will




Weak Bases
The conjugate base of an acid is the base that is formed when the acid has donated a hydrogen ion The conjugate acid of a base is the acid that forms when base accepts a hydrogen ion The 7 common strong acids are HCl, HBr, HI,Hydrogen iodide is a diatomic molecule and hydrogen halide Aqueous solutions of HI are known as hydroiodic acid or hydriodic acid, a strong acid Hydrogen iodide and hydroiodic acid are, however, different in that the former is a gas under standard conditions, whereas the other is an aqueous solution of the gas They are interconvertible HI is used in organic and inorganic synthesis asAcids and Bases For more than 300 years, substances that behaved like vinegar have been classified as acids, while those that have properties like the ash from a wood fire have been called alkalies or basesThe name "acid" comes from the Latin acidus, which means "sour," and refers to the sharp odor and sour taste of many acidsVinegar tastes sour because it is a dilute solution of
Common Causes Potential Result Potential Advice High Acid Number And/or Low Base Number Overheating Excessively extended drain interval Wrong lubricant High sulphur fuel Decreased BN Corrosion Oil Thickening and Sludging Increased wear Filter blocking Component Seizure Evaluate oil drain interval Establish new baseline BN / AN valuesHigh buffering capacities come from solutions with high concentrations of the acid and the base and where these concentrations are similar in value Practice weak acid problem C 6 H 5 COONa is a salt of a weak acid C 6 H 5 COOH A 10 M solution of C 6 H 5 COONa has a pH of 860Acids and Bases DrGergens !SD Mesa College •General Properties Periodic Trends •Acid Base (Strong versus Weak) •Acid Base Conjugates •Reactions Which is the stronger acid and why?
Conjugate acid → one hydrogen greater than BronstedLowry base Reaction given HI(aq) H2O(l) ⇌ H3O(aq) I(aq) % (337 ratings) Problem Details HI (aq) H 2 O (l) ⇌ H 3 O (aq) I (aq) Identify each as either a BronstedLowry acid, BronstedLowry Acid vs Base The difference between Acid and Base is their pH scale Acid has a pH scale lesser than neutral (7), whereas base has its scale higher than 7 After dissolving, acid does not change the color of the solution On the opposite, the base does change It turns pinkish in coloration The preceding is the contributor of a protonThus, small changes in pH represent large changes in the concentrations of hydrogen ions Pure water is neutral It is neither acidic nor basic, and has a pH of 70 Anything below 70 (ranging from 00 to 69) is acidic, and anything above 70 (from 71 to 140) is alkaline



Csun Edu




Acids And Bases I Introduction
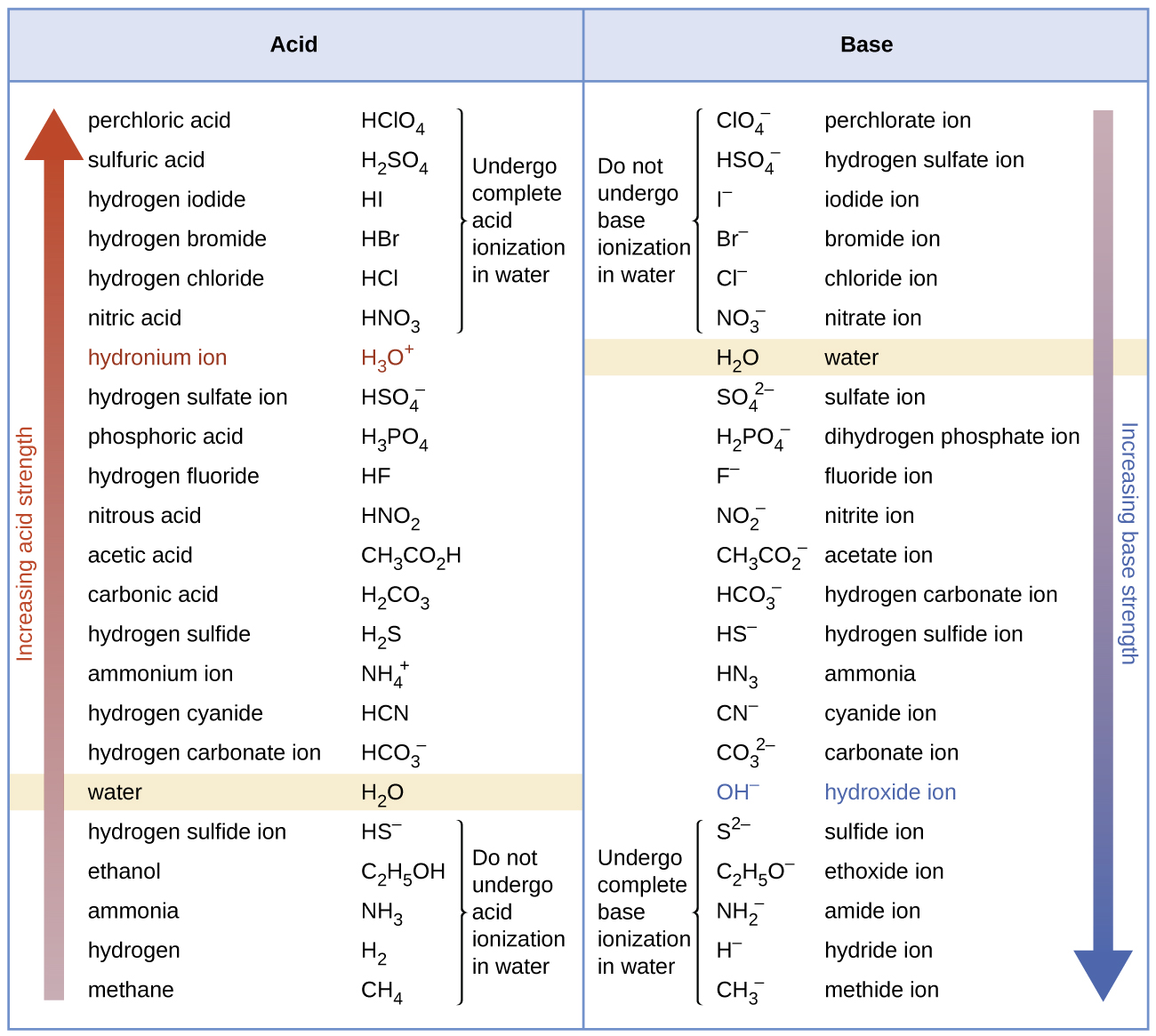
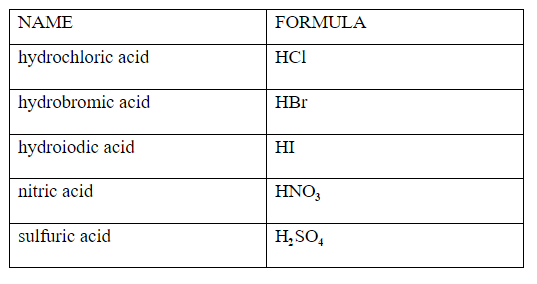
Identifying Conjugate AcidBase Pairs According to BronstedLowry theory, a conjugate acidbase pair consists of molecules or ions related by the loss of one H by an acid, an the gain of one H by a base Every acidbase reaction contains two conjugate acidbase pairs because an H is transferred in both the forward and reverse directions HI hydroiodic acid 301 4 108 HBr hydrobromic acid 301 4 108 HCl hydrochloric acid 301 4 108 HNO 3 nitric acid 301 4 108 H 3 PO 4 orthophosphoric acid 306 226 163 H 3 AsO 4 arsenic acid 308 231 170 H 2 SeO 3 selenous acid 315 247 190 H 2 CrO 4 chromic acid 303 233 6 H3Citrate citric acid, C 6 H 8 O 7 324 262 Citric (SITrik) acid is what makes orange juice sour Its chemical formula is a bit more complicated and is written as C 6 H 8 O 7 or CH 2 COOHC (OH)COOHCH 2 COOH or C 6 H 5 O 7 (3−) BrønstedLowry bases, in contrast, are good at stealing protons, and they'll gladly take them from acids One example of a base is ammonia




Solved Classify The Compounds As Acids Bases Or Salts Chegg Com




Hl Acids And Bases Strength Of Acids Bases Strong Acids 100 Ionized Or Dissociated Hcl Hbr Hi Hno 3 H 2 So 4 Hclo 4 Hclo 3 Strong Bases Ppt Download
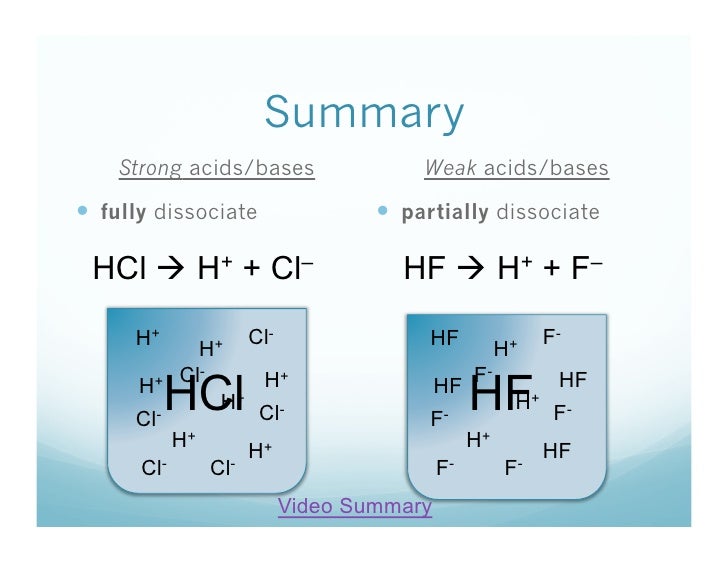
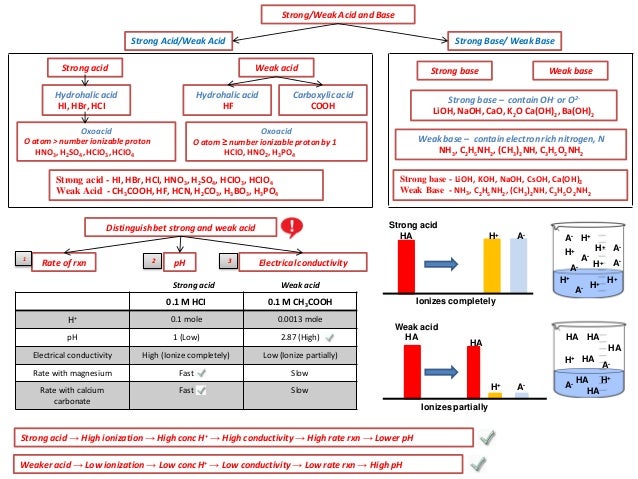
//wwwthinglinkcom/scene/ ACID (wikipedia) An acid is a molecule or ion capable of donating a hydron (proton or hydrogen ion H), or, alternatively, capable of forming a covalent bond with an electron pair (a Lewis acid) BASE (wikipedia)(favors weaker acid) 3 CH 3CH 2OH acid pK a 16 CH 3NH 2 conj acid pK a 38 Eq forward ! In chemistry, there are seven "strong" acids What makes them "strong" is the fact that they completely dissociate into their ions (H and an anion) when they are mixed with waterEvery other acid is a weak acidBecause there are only seven common strong acids, it is easy to commit the list to memory



What Are Strong Acids Or Bases Are That Ionize Or Dissociate In Aqueous Solution Socratic



Acids
Explanation The pH scale formally runs from 0 to 14, where 0 is the most acidic, while 14 is the most alkali A solution can be considered either acidic, neutral, or basic Let the solution's pH be x If 0 ≤ x < 7, then the solution is acidic If 7 < x ≤ 14, then the solution is basic If x = 7, then the solution is neutralAnswer (1 of 2) Hi, CCl4 is called carbon tetrachloride, or more commonly and in an abusive denomination "tetrachloromethane" (abusive, as it is not methane, not even in part) CCl4 is a liquid solvant at (T, p)n, and does not burn in these conditions ItsPage 3 PREDICTING ACIDBASE PRODUCTS AND EQUILIBRIUM DIRECTION 7!Use a pK a table to determine the direction of the equilibrium for these acidbase reactions a!HF NH 3 F – NH 4 HF acid pK a 32 NH 4 conj acid pK a 92 Eq forward !




Aim How To Understand Acid Base Reactions Do




The Preparations Of Two Aqueous Solutions Are Described In T Clutch Prep
Arrhenius Definition Acid is a kind of chemical compound that when dissolved in water gives a solution with H ion activity more than purified water A base is an aqueous substance that donates electrons, accept protons or release hydroxide (OH) ions 2 "Acid base "rarr" salt and water" And thus HI(aq) KOH(aq) rarr KI(aq) H_2O(l) Because the potassium and iodide salts are along for the ride, we could write the net ionic equation as H^ HO^() rarr H_2O(l) OR H_3O^ HO^() rarr 2H_2O(l) Are "mass" and "charge" balanced in each instance? A pH of 0 indicates a high level of acidity A pH of 7 is neutral A pH of 14 is the most basic, or alkaline The distance between two points on the pH
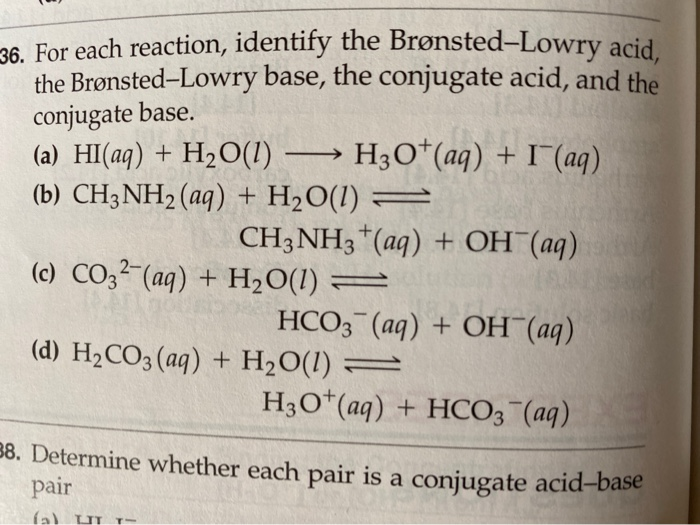



Solved 36 For Each Reaction Identify The Bronsted Lowry Chegg Com




Weak Bases
This reaction involves a strong acid (HI) and a strong base (LiOH) The hydroxide ion and the hydrogen ion will combine to form water Therefore, theAmphoterism The ability of a substance to act as an acid and a base Ex HSO4−, for example, can donate H to become SO42− (acting as an acid), or it can accept H to become H2SO4 (acting as a base) Water as an amphoteric acts as an acid to form OH− Water acts as a base to form H3O Thus, water is amphotericHistorically, the first chemical definition of an acid and a base was put forward by Svante Arrhenius, a Swedish chemist, in 14 An Arrhenius acid A compound that increases the hydrogen ion concentration in aqueous solution is a compound that increases the H ion concentration in aqueous solution The H ion is just a bare proton, and it is rather clear that bare protons are not



Which Of The Following Is Acidic Basic Or Neutral Mgcl2 K3bo3 Naso4 Quora




16 1 Acid Base Equilibria Youtube
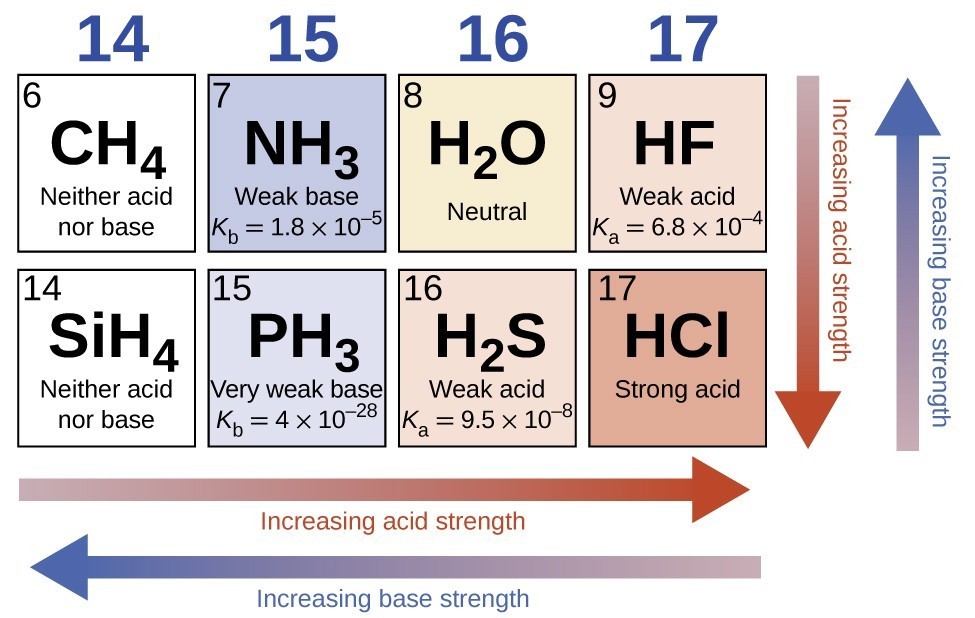
HCl or HI H 2 O or H 2 S H 2 S or HCl I is a larger atom with a more easily broken HI bondHistorically, the first chemical definition of an acid and a base was put forward by Svante Arrhenius, a Swedish chemist, in 14 An Arrhenius acid A compound that increases the hydrogen ion concentration in aqueous solution is a compound that increases the H ion concentration in aqueous solution The H ion is just a bare proton, and it is rather clear that bare protons are notIf they are not, you know that it cannot be accepted as a representation of




Hi H2o Hydroiodic Acid Water Youtube




Acid And Bases Guide Acid Base Study Guide Acid Proton Donor Base Proton Acceptor We Write The Studocu
TABLE OF CONJUGATE ACIDBASE PAIRS Acid Base K a (25 oC) HClO 4 ClO 4 – H 2 SO 4 HSO 4 – HCl Cl– HNO 3 NO 3 – H 3 O H 2 O H 2 CrO 4 HCrO 4 – 18 x 10–1 H 2 C 2 O 4 (oxalic acid) HC 2 O 4 – 590 x 10–2 H 2 SO 3 = SO 2 (aq) H2 O HSOHI Strong Acid (Hydroiodic Acid) HClO4 Strong Acid (Perchloric Acid) H2SO4 Strong Acid (Sulfuric Acid) HNO3 Strong Acid (Nitric Acid) HF Weak Acid (Hydrofluoric Acid) HNO2 Strong/Weak Acids and Bases 38 terms Zoe0907 OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR Genetics Final 150 terms mepelehac Genetics Lecture 10 29 terms mepelehac L10Answer (1 of 3) A substance wwhich has a tendency to accept a proton is base and which has tendency to donate proton is acid OH contains unpaired electron on which any proton can easily attack Thus it has a tendency to accept proton therefore, it's a




Weak Acids Bases Have Ka Kb And Rice Ppt Download



Acids Bases And Buffers Bagnechem
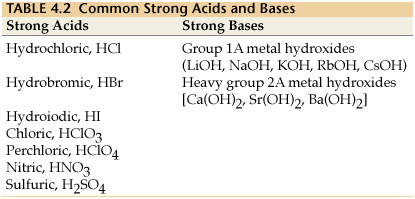
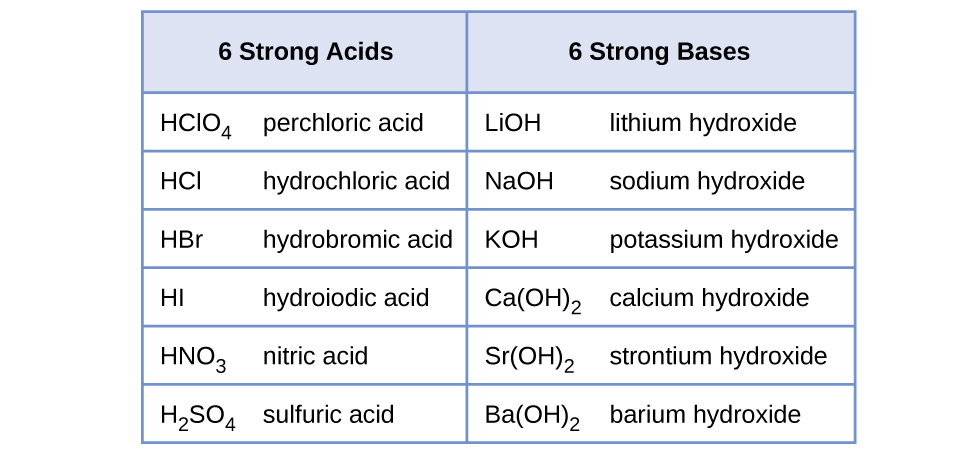
There are six common stron acids HNO3,HClO4,H2SO4,HCL,HBr,HI and strong base are all the group Ist hydroxides and the Three of group 2 hydroxides Ca(OH)2, Sr(OH)2 and Ba(OH)2 Answer HClO is an acid as is has the proton that it can donate but it is a weak acid because it is not one the acid amoung the list of the strong acids The next most common acidic household item may be muriatic acid Muriatic acid is used to lower the pH of swimming pool water if it climbs too high It's also excellent for tough jobs, like cleaning masonry work Wear goggles and gloves when handling muriatic acid and always dilute it by adding acid to the water Never add water to the acidCh3ch2cooh is Acid I'll tell you the Acid or Base list below If you want to quickly find the word you want to search, use Ctrl F, then type the word you want to search List molecules Acid and Base LIST ACID acetaminophen Acid acetone Acid




Acids And Bases Boundless Chemistry




Acid Base Basics Seminars In Nephrology
In acidbase chemistry, titrations can be used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution Explore titration, titrant, neutralization reaction and equivalence point, and how toIn chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis basesAll definitions agree that bases are substances which react with acids as originally proposed by GF Rouelle in the mid18th century Svante Arrhenius proposed in 14 that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to formWe see the same pattern in the chemistry of compounds that contain the OH, or hydroxide, group Metal hydroxides, such as LiOH, NaOH, KOH, and Ca (OH) 2, are bases Nonmetal hydroxides, such as hypochlorous acid (HOCl), are acids The table below summarizes the trends observed in these three categories of compounds



Umsl Edu




Is Hi A Strong Acid Techiescientist
14 Acid – Base strength and hardness and softness 15 Application and limitations of HSAB principle Introduction The Lewis concept failed to provide a definite and uniform scale to measure the relative strength of acids and bases The Lewis definition recognizes acid and bases in terms of their ability to accept or donate electron pairsThe ammonium ion(NH 4 ) is an acid in nature as it releases the proton when dissolved in an aqueous solution However, it is a very weak acid having a pH value of 55 ie near to neutral in the acidbase scale The proton donating abilityAnswer HI ( Hydrogen iodide ) is strong acid What is an acid, base, neutral ?



Acids And Bases




Solved Write The Formula For The Conjugate Base For Each Of The Following Acids Hci Hi Hno Hcio
6 rows HI is acid as it liberates the H ions when dissolved in aqueous solution and increase theAldehyde acid pK a 17 H 2CO 3 conjOne of the simpler acid base theories states that acids donate H ions and bases donate OH ions When HCN (Hydrogen cyanide) dissolves in water it breaks a



Relative Strengths Of Acids And Bases Chemistry Atoms First



14 3 Relative Strengths Of Acids And Bases Chemistry
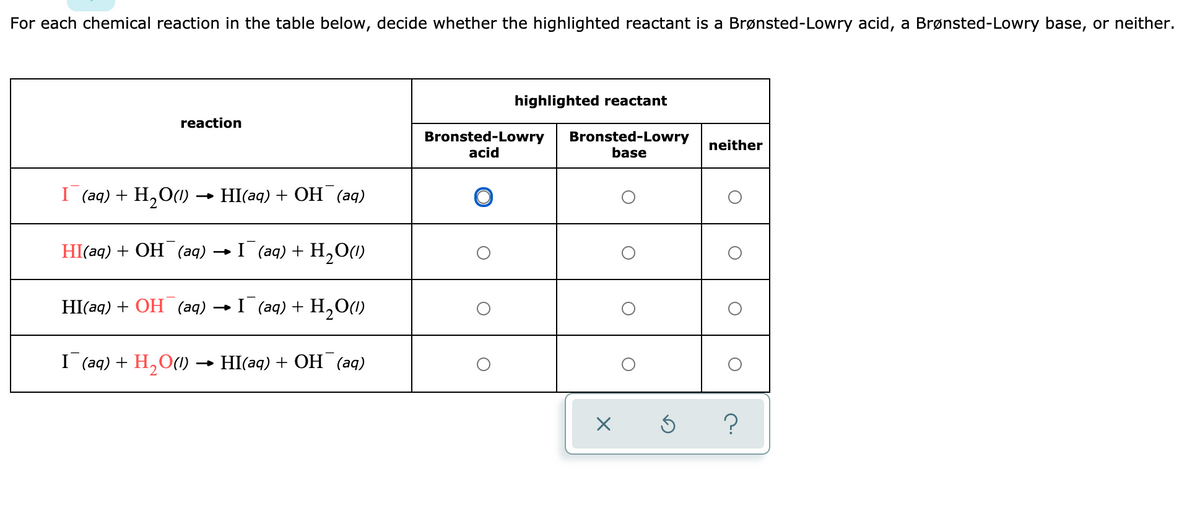



Answered For Each Chemical Reaction In The Table Bartleby




Analytical Chemistry Volumetric Analysis Chapter 4 Dr Salwa Albohy Ppt Download




List Of Strong Weak Acids Bases Chemistry Basics Chemistry Organic Chemistry



1 22 What Are Strong Acids And Bases



14 3 Relative Strengths Of Acids And Bases Chemistry



Ib Chemistry On Acid Base Buffers



Sanjac Edu




Chapter 14 Lecture Basic Chemistry Fourth Edition 14
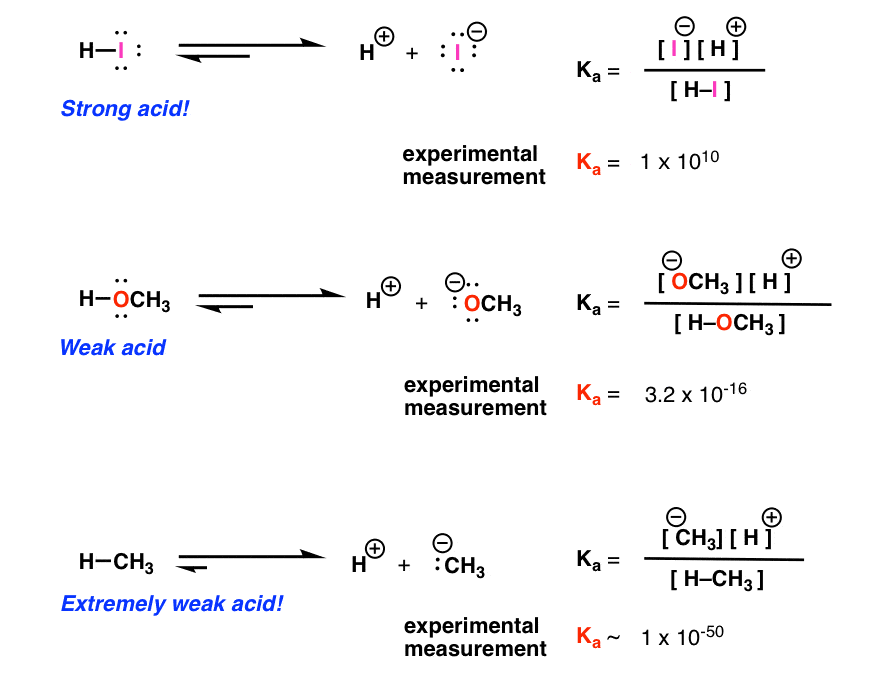



Acid Base Reactions Introducing Ka And Pka Master Organic Chemistry



What Are Some Examples Of Strong And Weak Acids And Bases Quora




How To Write The Net Ionic Equation For Hi Ba Oh 2 Bai2 H2o Youtube




Is Hi A Strong Acid Techiescientist




Is Hi An Acid Or Base Strong Or Weak Hydroiodic Acid




Classify The Compounds As A Strong Acid Weak Acid Strong Base Or Weak Base Strong Acid Homeworklib




10 Acid Base Equilibria Titrations Flashcards Quizlet



1




Hepatobiliary Acid Base Homeostasis Insights From Analogous Secretory Epithelia Journal Of Hepatology



Acid Base Character Of Oxides And Hydroxides Chemistry Libretexts
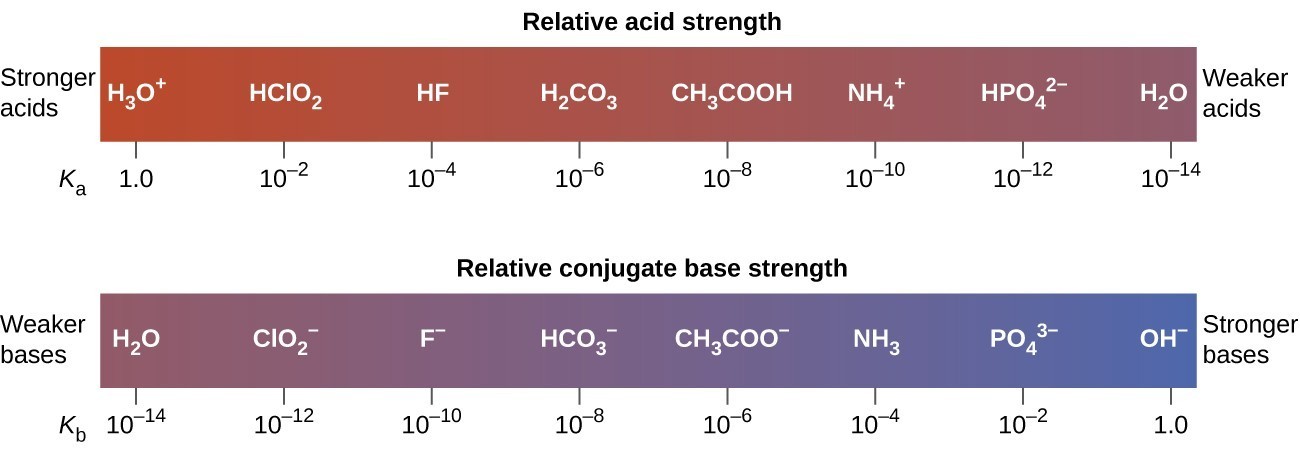



Relative Strengths Of Acids And Bases Chemistry Atoms First




Conjugate Acid Base Pairs Video Khan Academy




Blank08s3
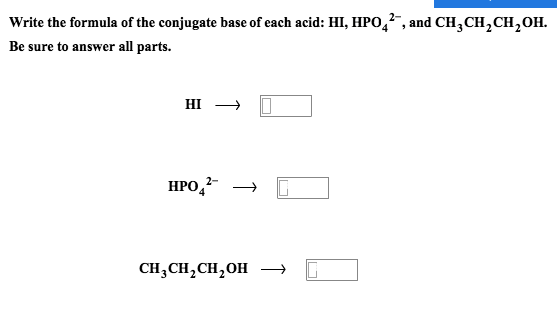



Solved Write The Formula Of The Conjugate Base Of Each Acid Chegg Com
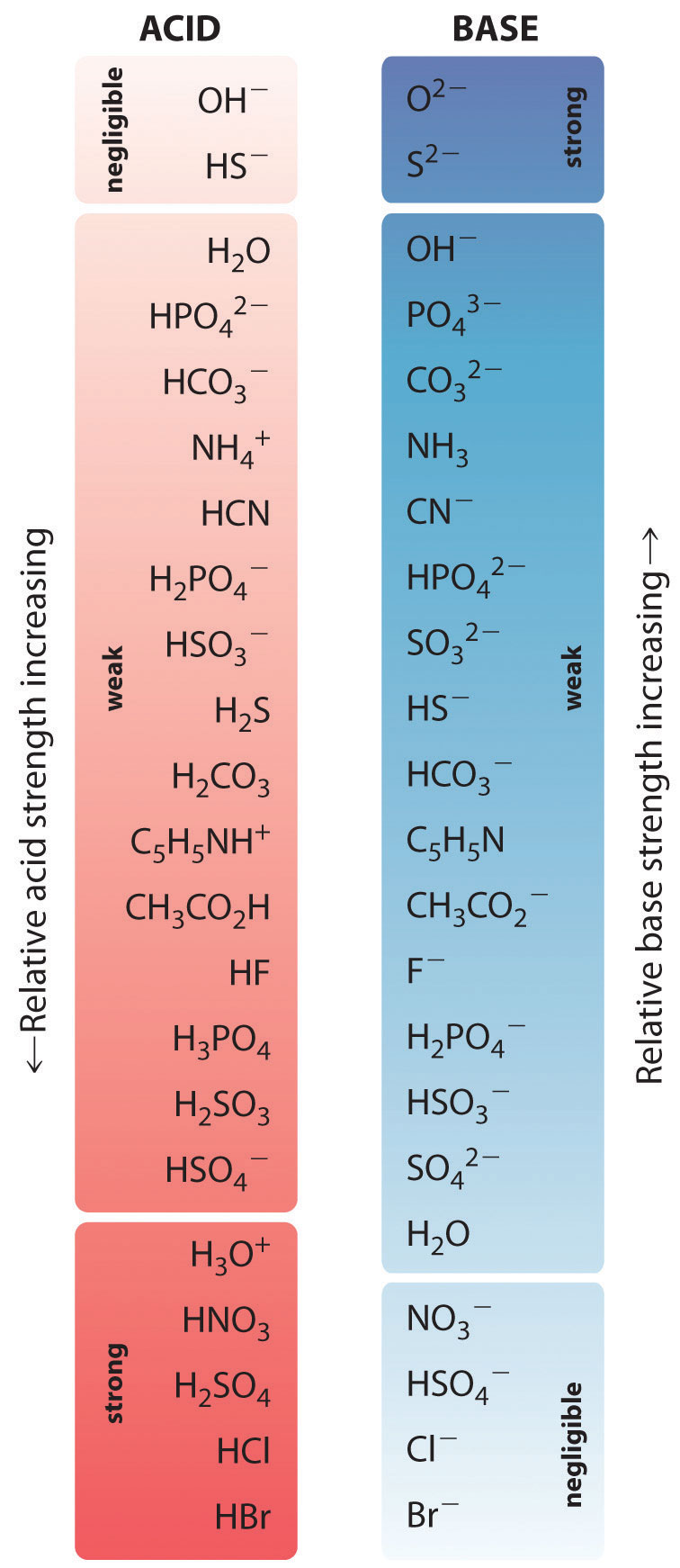



16 6 Finding The H3o And Ph Of Strong And Weak Acid Solutions Chemistry Libretexts




Answered For Each Chemical Reaction In The Table Bartleby




Relative Strength Of Acids Chemistry Notes



Spscc Instructure Com




9 1 Introduction To Acids And Bases Ppt Download
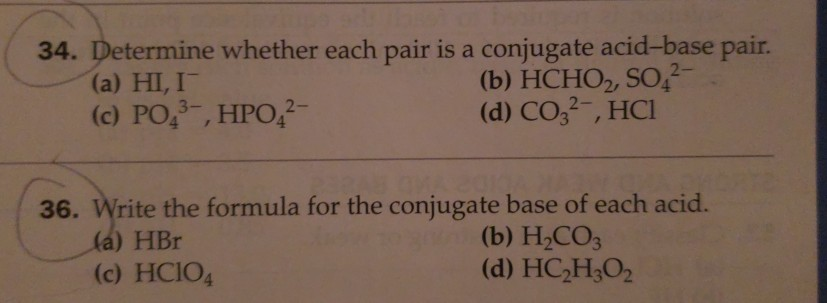



Solved 34 Determine Whether Each Pair Is A Conjugate Chegg Com




Hi There My Name Is Renata I M An Img International Medical Graduate From Peru These Are My Nursing School Nursing School Survival Nursing School Tips



1




Classify Each Chemical Compound Listed In The Table Below Type Of Compound Check All That Brainly Com




Is Hi An Acid Or Base Strong Or Weak Hydroiodic Acid
/list-of-strong-and-weak-acids-603642-v2copy2-5b47abd0c9e77c001a395e55.png)



List Of Common Strong And Weak Acids




Acid Base Packet 1



Solved Classify Each Chemical Compound Listed In The Table Below Type Of Compound Check All That Apply Compound Ionic Molecular Acid Base H Course Hero




Mcat General Chemistry Acids And Bases Flashcards Quizlet




Get Answer Reaction Cl Ag H30 Ag Hch3co2 Nh3 Aq Ch3 Co2 Nh4 Transtutors




Acids Bases
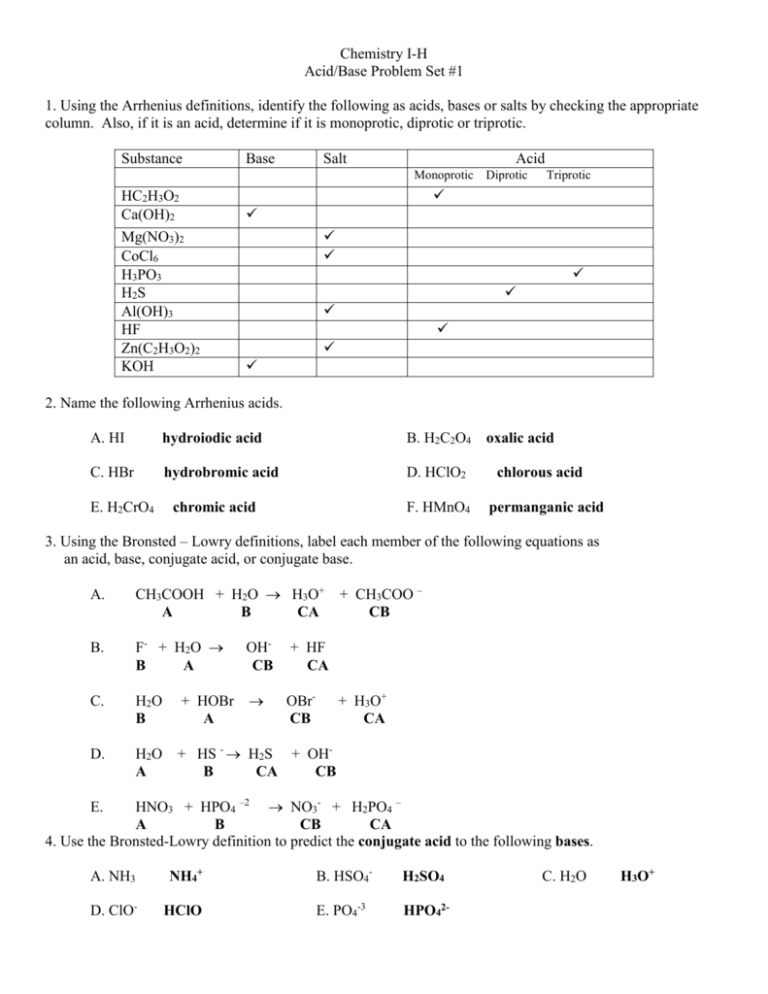



Acid Base Problem Set 1
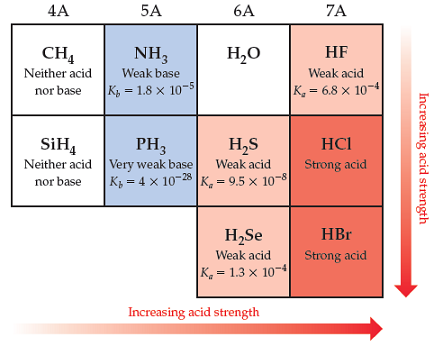



Solved Part A Are The Acid Properties Of Hi What You Chegg Com




Strong Acid Solutions Video Khan Academy



Weak Acids And Bases



1
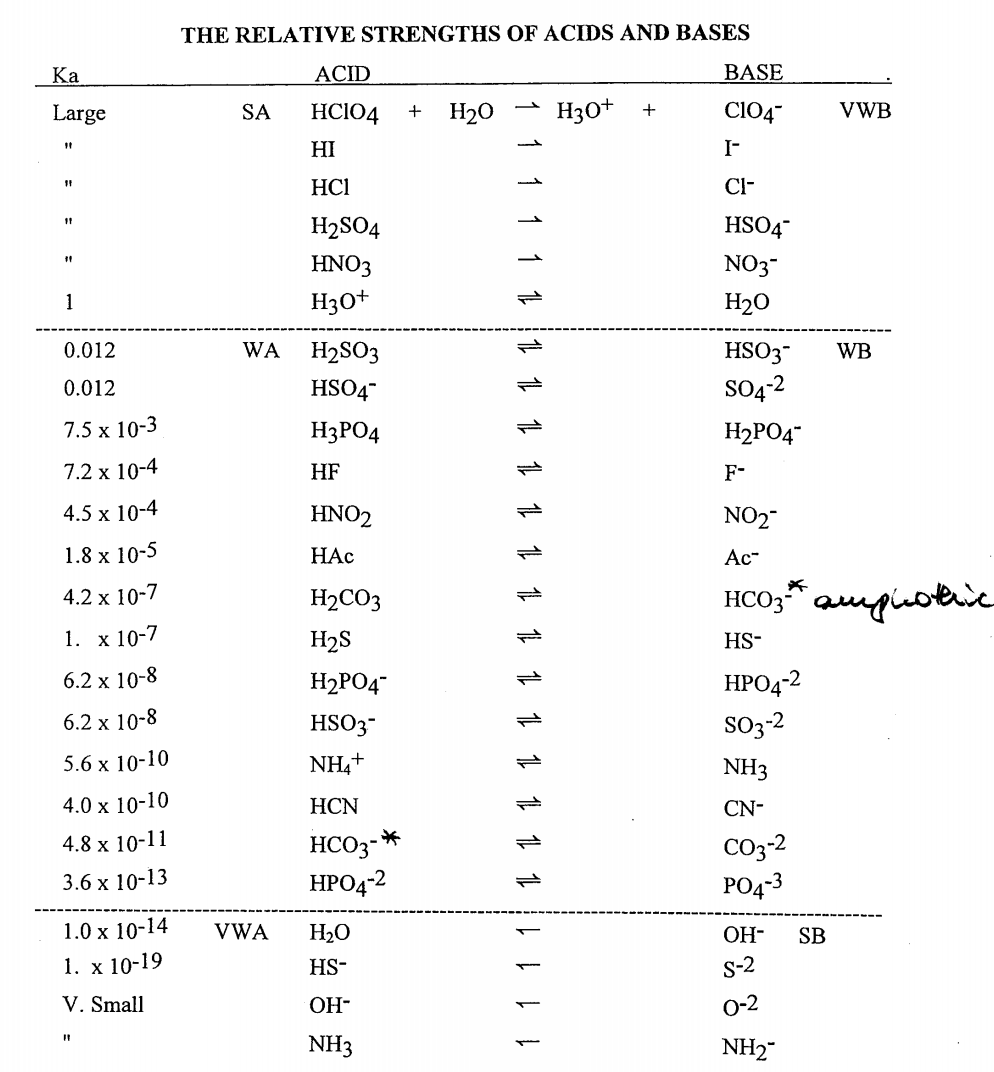



Solved The Relative Strengths Of Acids And Bases Ka Acid Chegg Com




Is Hi Hydroiodic Acid A Strong Or Weak Acid Youtube



Ppt Reactions In Aqueous Solution Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Blamp Sites Truman Edu



Acid And Base Scienceaid




Is Hi An Acid Or Base Strong Or Weak Hydroiodic Acid




Strong And Weak Acids And Bases Biology




Acids And Bases I Introduction




Acids Bases And Salts According To Arrhenius Theory Acid Base Salt Water Examples Hcl Naoh Nacl H 2 O H 2 So 4 Sr Oh 2 Srso 4 2h Ppt Download




Chapter 10 Acids Bases Characteristics Of Acids Sour
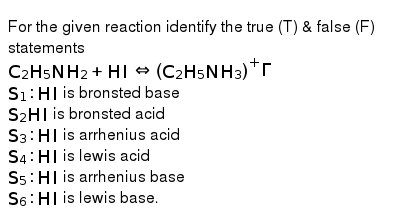



For The Given Reaction Identify The True T False F Statements C 2 H 5 Nh 2 Hiharr C 2 H 5 Nh 3 Gamma S 1 Hi Is Bronsted Base S 2 Hi Is Bronsted Acid S 3 Hi Is Arrhenius Acid S 4 Hi Is Lewis Acid S 5 Hi Is




Chem 1180 15 1 15 8 All Of Chapter 15




Tips For Identifying Acid And Base Strength Concept Chemistry Video By Brightstorm



Strong Acids Acid Base Education
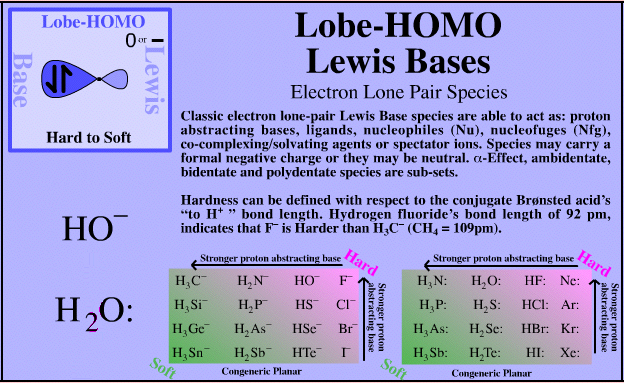



Clickable Lewis Acid Base Matrix Chemogenesis




Is Hi An Acid Or Base Strong Or Weak Hydroiodic Acid
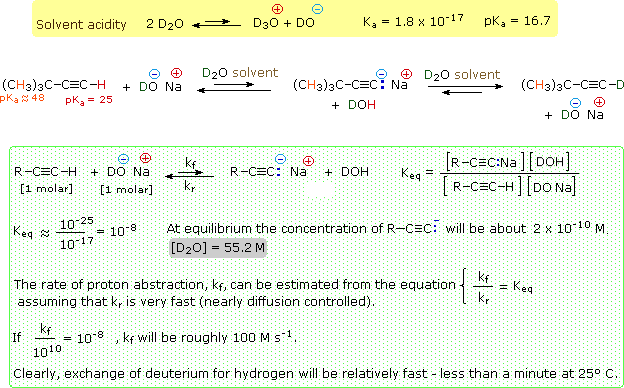



Acids Bases
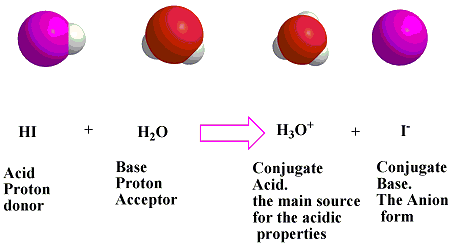



Which Pair Is A Bronsted Lowry Conjugate Acid Base Pair Nh 3 Nh 4 Or H 3o Oh Or Hcl Hbr Or Clo 4 Clo 3 Socratic




Lee Marek S Website Advanced Placement Class Notes Chapter 14



Neutralization Reactions Acids And Bases Pathways To Chemistry
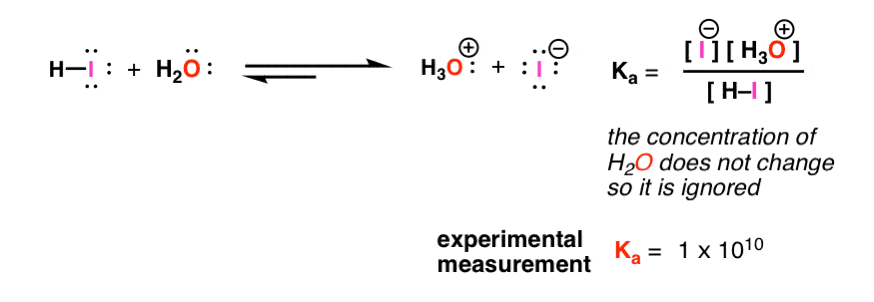



Acid Base Reactions Introducing Ka And Pka Master Organic Chemistry




Acid Base Reactions Definitions Strong Acids Hcl Hbr Hi Hno 3 Hclo 4 H 2 So 4 Acid A Species That Supplies H Ions To Water Strong Acid Ppt Download



Web Gccaz Edu



Ion Chem Usu Edu




Label The Conjugate Acid Base Pairs In Each Equation A Hi Aq Nh3 Aq Nh Aq Aq Guid Homeworklib
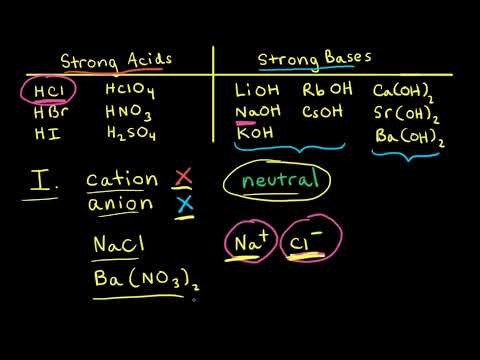



Acid Base Properties Of Salts Video Khan Academy




Chemistry Guide The Quick Guide To Acids And Bases By Forum E Forum Education Guidebooks Medium



Classify Each Substance As A Strong Acid Strong Base Weak Acid Or Weak Base Home Work Help Learn Cbse Forum



Yorku Ca




Silpsknvupdtkm




Strong Acids And Bases Cheat Sheet Study Guide Mcat And Organic Chemistry Study Guides Tutoring




Classify Each Substance As A Strong Acid Clutch Prep




Acid Base Nomenclature Diagram Quizlet




Acids And Bases Intro Acidbase Definitions Q Arrhenius




In Aqueous Solution Classify These Compounds As Strong Acids Weak Acids Strong Bases Weak Bases Or Homeworklib



Solved B What Is The Main Conjugate Acid Base Pair What Is The Other Conjugate Acid Base Pair C Is Butanoic Acid A Strong Or Weak Electrolyte D Would The Addition Of Hydronium Ions Cause




Identifying A Compound As A Bronsted Acid Base Both R Chemhelp



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿